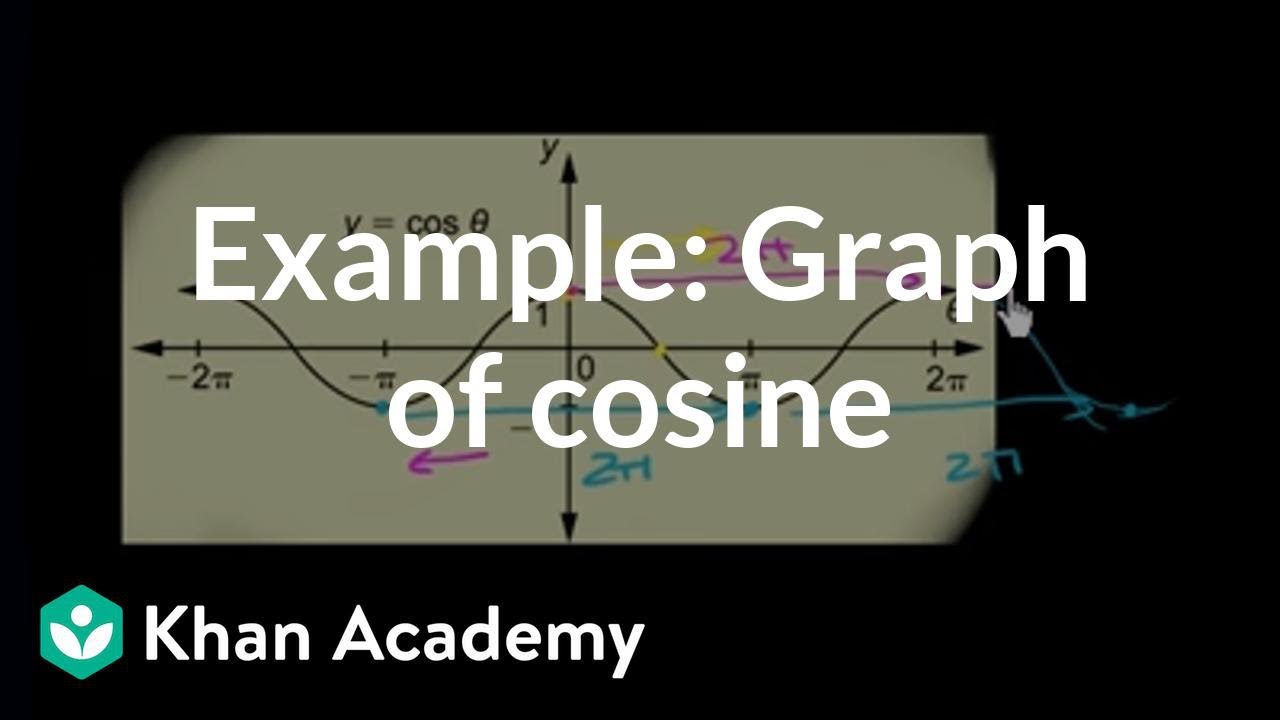
Proof of sin (π/2θ)=cosθ upto cosec (π/2θ)=secθ using Euler's formula If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch Since the point B B can be anywhere along the unit circle in the first and fourth quadrants, it follows that the angle ϴ= ∠BOA ϴ = ∠ B O A can vary over values in between −π 2 − π 2 and π 2 π 2 We can represent this possible range of values of ϴ ϴ by writing the inequalities −π 2 < ϴAnswer to which of the following shows that sin(π2θ)Cos θ = 0 a) sin(π2θ)=Cos θ, so sin(π2θ)Cos θ = Cos θ Cos θ

The Value Of T A Nthetasin Pi 2 Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Is 1 B 1 C 1 2sin2theta D None Of These
Sin(θ+π/2)=cosθ 证明
Sin(θ+π/2)=cosθ 证明-I want to know how to solve these kind of problems so please don't just show me the answer公式の導き方を覚えちゃえば楽勝だよ! ひとつひとつの公式を覚えていっても良いのですが結構大変です (^^;) 今回は三角関数の中でも、 や の形をした三角関数の公式とその導き方を伝えていきます。 記事の内容 ・θ+π/2,θπ三角関数の公式まとめ




Engineering Mathematics I Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
The (π/2θ) formulas are similar to the (π/2θ) formulas except only sine is positive because (π/2θ) ends in the 2nd Quadrant sin(π/2θ) = cosθ cos(π/2θ) = sinθ tan(π/2θ) = cotθ cot(π/2θ) = tanθ Proof The Trigonometric ratios of angle (θ)Proportionality constants are written within the image sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, where θ is the common measure of five acute angles In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a rightangled triangle to ratios of two side lengthsTo remember the trigonometric values given in the above table, follow the below steps First divide the numbers 0,1,2,3, and 4 by 4 and then take the positive roots of all those numbers Hence, we get the values for sine ratios,ie, 0, ½, 1/√2, √3/2, and 1 for angles 0°, 30°, 45°, 60° and 90°
Sol (1 – sinθ cosθ) 2 = 1 sin 2 θ cos 2 θ – 2sinθ 2cosθ – 2sinθcosθ = 2 – 2sinθ 2cosθ – 2sinθcosθ = 2 (1 – sinθ) 2 cosθ (1 – sinθ) = 2(1 – sinθ)(1 cosθ) = RHS Example 16 If sinθ sin 2 θ = 1, prove that cos 2 θ cos 4 θ = 1 Sol We have, sinθ sin 2 θ = 1 ⇒ sinθ = 1 – sinFor polar equation r = cos(θ) sin(2θ) , when r=0 the θ values are 3π/2, π/2, 7π/6, and 11π/6 But when I simplify the equation to 2sin(θ) = 1, using trig identity sin(2θ) =2sinθcosθ, I Explanation using appropriate Addition formula ∙ sin(A± B) = sinAcosB ± cosAsinB hence sin( π 2 − θ) = sin( π 2)cosθ − cos( π 2)sinθ now sin( π 2) = 1 and cos( π 2) = 0 hence sin( π 2)cosθ − cos( π 2)sinθ = cosθ − 0
Math 109 T6Exact Values of sinθ, cosθ, and tanθ Review Page 2 61 By memory, complete the following table θ 0 π 6 π 4 π 3 π 2 2π 3 3π 4 5π 6 π 3π1 sinθ= cos(π/2θ) 2 cosθ= sin(π/2θ) 3 tanθ= cot(π/2θ) 4 cotθ= tan(π/2θ) 5 secθ= csc(π/2θ) 6 cscθ= sec(π/2θ)Suppose sin θ=2/3 where π < θ < 3 π/2 Find cos θ and tanθ Who are the experts?




2 Sin Pi4 Theta Costheta Sintheta




Trigonometric Functions Justin Skycak
How to find Sin Cos Tan Values?Math 1330 Section 43 Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axisPositive angles are measured counterclockwise from the initial sideNegative angles are measured clockwiseWe will typically use the Greek letter θ to denote an angle How do I prove that secθ tanθsinθ = cosθ So far I have LS 1/cosθ sinθ/cosθ (sinθ) =1/cosθ sin^2/cosθ math If sinθ=7/13 and cosθ=12/13 find tan θ and cot θ Use Pythagorean Identities to find sin θ and tan θ if cos θ =24/25 if the terminal side of θ lies in the third quadrant
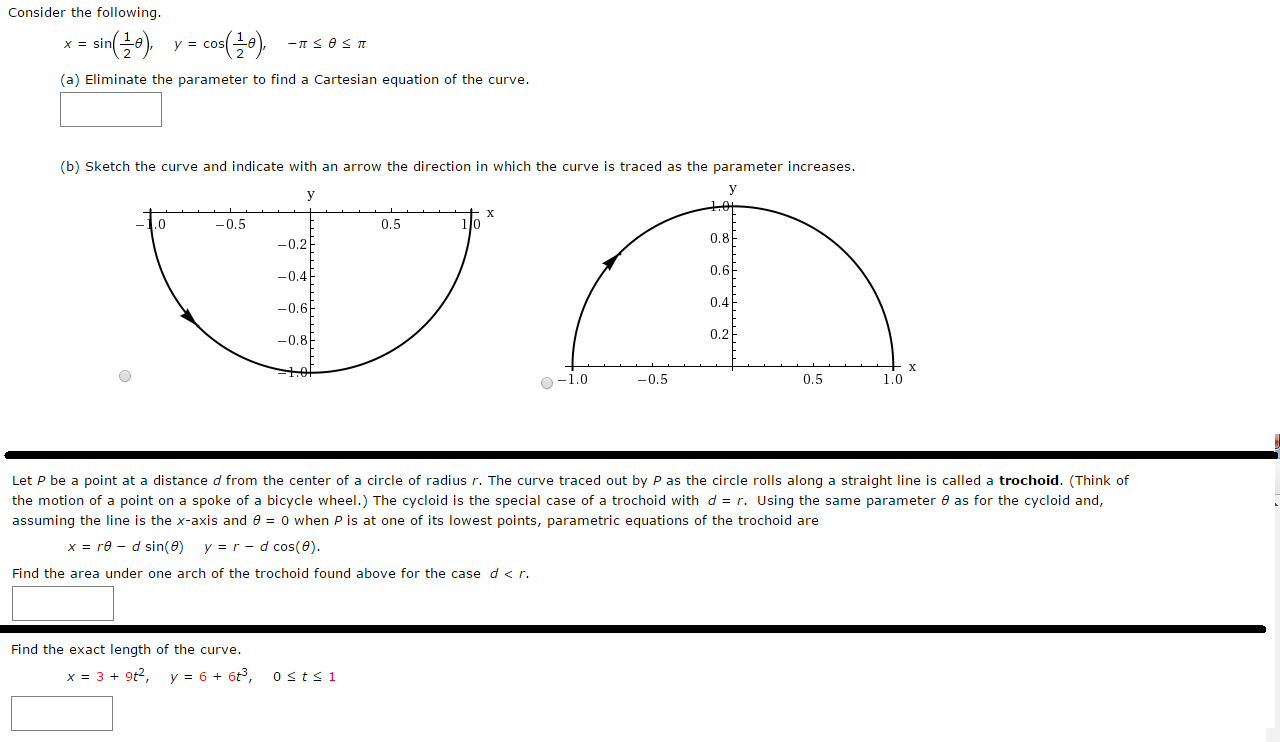



Consider The Following X Sin 1 2 Theta Y Chegg Com




Ex 6 2 9 Prove That Y 4 Sin 2 Cos Theta Is Increasing
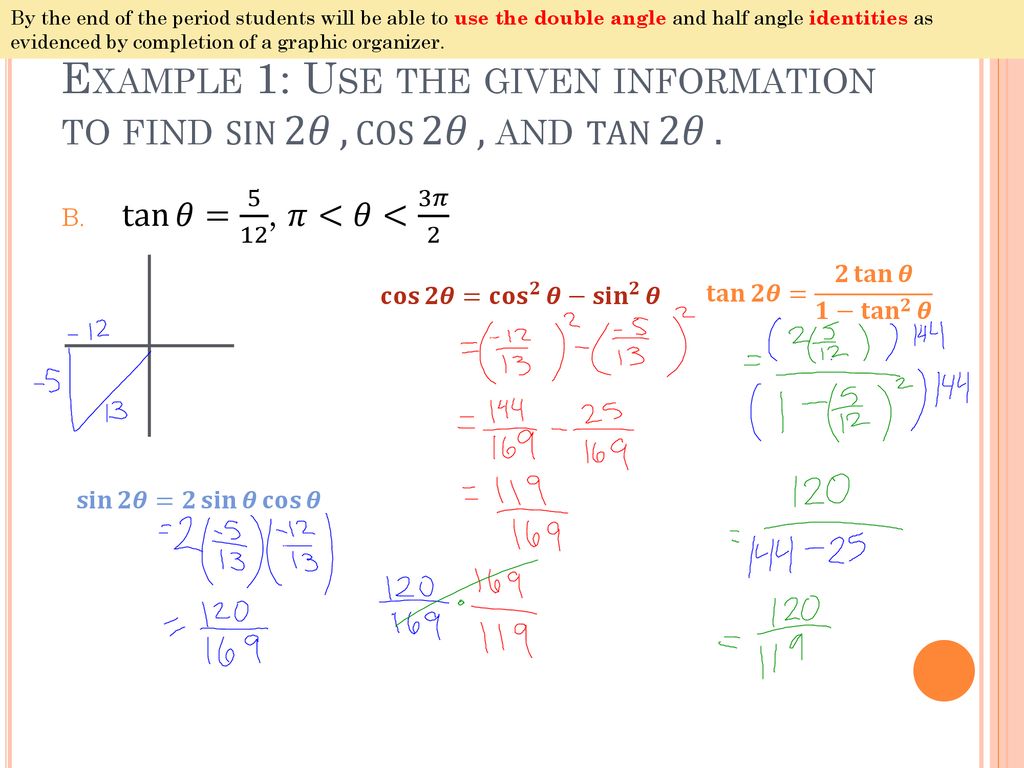
This problem has been solved!Question Find the exact values of sin 2θ, cos 2θ, and tan 2θ for the given value of θ cos θ = 3/5;Cosθ(2cosθ 1) = 0 ⇒ cosθ = 0, cosθ = − 1 2 The solutions are θ = π 2, 3π 2 and θ = 2π 3, 4π 3 7 Solve 2sin2 θ −sinθ −1 = 0 on the interval 0 ≤ θ < 2π 2sin2 θ −sinθ −1 = 0 (2sinθ 1)(sinθ −1) = 0 ⇒ sinθ = − 1 2, sinθ = 1 The solutions are θ = 7π 6, 11π 6 and θ = π 2 13 Solve sin2 θ = 6(cosθ 1) on the interval 0 ≤ θ < 2π



Www Math Uh Edu Jiwenhe Math1432 Lectures Lecture13 Handout Pdf




2 Given That Cos 8 3 5 Find That 8 Is Gauthmath
Trigonometry functions calculator that finds the values of Sin, Cos and Tan based on the known values All the six values are based on a Right Angled Triangle Code to add this calci to your website Just copy and paste the below code to your webpage where you数式を読みやすくするための便宜です。私は日常的に sin,cos,tan,sec,cosec,cotan あたりを使っています。 たとえば次の問題: まず、ABを半径とする半円の中心からT,Uに引いた長さは半径。 さらに頂点Dから見ると、DU=AD(=BC)、さらにTおよびUをαからみると nx2x (それぞれ目盛りを2つ引いていTrigonometric Identities Trigonometric identities are equations involving the trigonometric functions that are true for every value of the variables involved Some of the most commonly used trigonometric identities are derived from the Pythagorean Theorem , like the following sin 2 ( x) cos 2 ( x) = 1 1 tan 2 ( x) = sec 2 ( x)




How Can The Maximum Value Of F Theta 5 Cos Theta 3 Cos Theta Pi 3 Be 10 Mathematics Stack Exchange




Versine Wikipedia
Add sin^2(theta) to both sides Divide both sides by 2 Apply the square root to both sides Multiply top and bottom by sqrt(2) to rationalize the denominator Apply the arcsine, or inverse sine, to both sides Use the unit circle Note that sin(pi/4) = sqrt(2)/2 We were originally told that , and we just found Intersect those two intervals to get = 2/cosθ Since π/2 < θ < π ,where cosθ is negative So, 2/cosθ Hence, LHS = RHS (Proved) Question 26 (i) If T n = sin n θ cos n θ, prove that \frac{T_3T_5}{T_1}=\frac{T_5T_7}{T_5} Solution LHS = = sin 2 θcos 2 θ RHS = = = sin2θcos 2 θ Question 26 (ii) If T n = sin n θ cos n θ, prove that 2T 6 – 3T 4 1 = 0 Solution0 votes 1 answer Let α and β be the roots of the quadratic equation x^2 sinθ– x(sinθcosθ 1) cosθ = 0 (0 < θ< 45º), and α < β



How Do You Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sin X Socratic



If Sin Pi Cos Theta Cos Pi Sin Theta Then Sin 2theta Youtube
Use the figures to evaluate the function given that f (x) = sin x, g (x) = cos x, and h (x) = tan x asked in PRECALCULUS byUse the fact that θ is a constant when computing limits as h goes to 0 The limit \lim_ {\theta \to 0}\frac {\sin (\theta )} {\theta } is 1 The limit lim θ → 0 θ s i n ( θ) is 1 To evaluate the limit \lim_ {h\to 0}\frac {\cos (h)1} {h}, first multiply the numerator and denominator by \cos (h)1 To evaluate the limit lim h → 0 h c oRaise sin ( θ) sin ( θ) to the power of 1 1 Use the power rule a m a n = a m n a m a n = a m n to combine exponents Add 1 1 and 1 1 Rewrite using the commutative property of multiplication Multiply − cos ( θ) ( − cos ( θ)) cos ( θ) ( cos ( θ))




Why Is Cos Pi 6 The Same As Cos Pi 6 Socratic



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Find the Other Trig Values in Quadrant I sin (theta)=12/13 sin(θ) = 12 13 sin ( θ) = 12 13 Use the definition of sine to find the known sides of the unit circle right triangle The quadrant determines the sign on each of the values sin(θ) = opposite hypotenuse sin ( θ) = opposite hypotenuse Find the adjacent side of the unit circleProve that cosθ/sin(90° θ) sin(θ)/sin(180° θ) tan(90° θ)/cotθ = 3 asked 8 hours ago in Trigonometry by Anaswara ( 224k points) trigonometric functionsBecause sin(π/2θ)=cosθ, and because the cosine of a negative angle is positive Hence, from 402 and 401 4,03 From the diagram we can find DO, segments of the line DE 404 From the definitions of the sine and cosine in ΔDBO ΔOBA 405 Substituting in equation 403, we find 406 We also note that in ΔOBA, the following
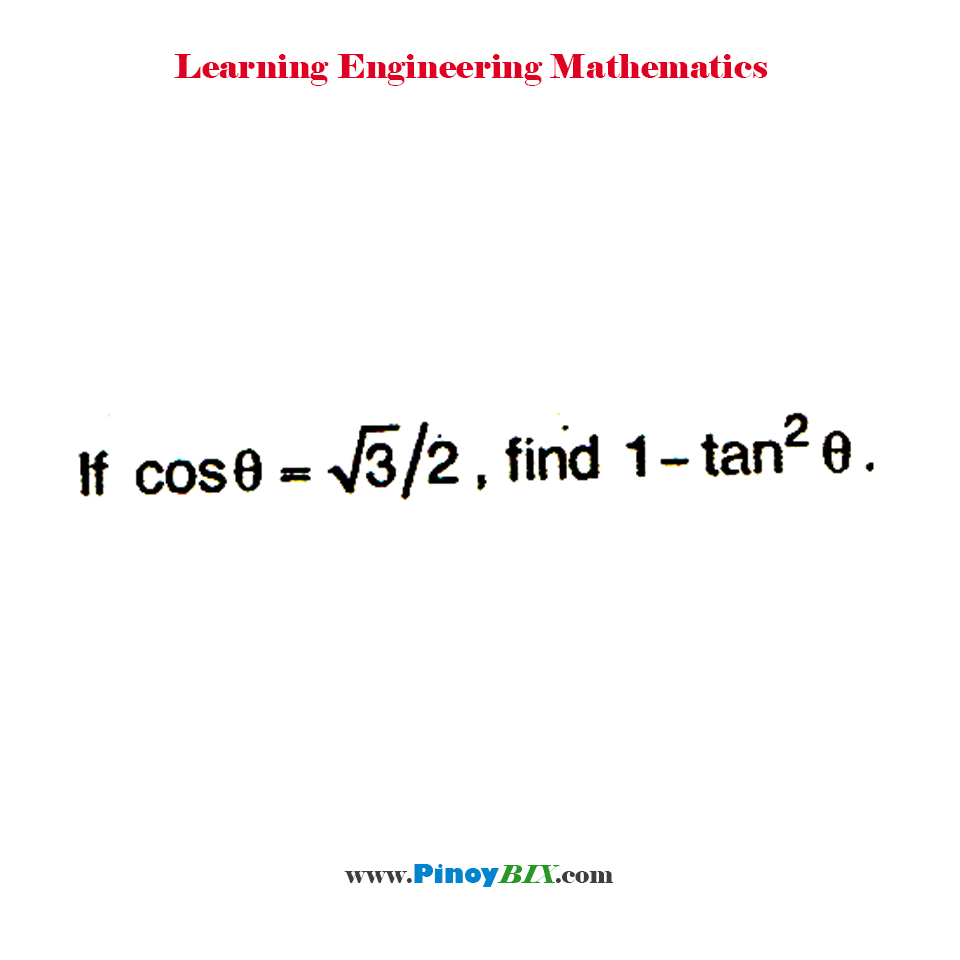



Solution If Cos8 3 2 Find 1 Tan 2 8




7 If Cos Theta Frac 12 13 0 Theta Frac Pi 2 Find The Value Of Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta Frac Sin 2 Theta Cos 2 Theta 2 Sin Theta Cos Theta Cdot Frac 1
π/2−θの三角関数の公式 これらの公式を利用して、次の公式を証明してみましょう。 公式の証明は加法定理を用いておこなうこともできますが、今回は加法定理を学習していなくてもできる方法で行います。 sin(π/2−θ)=cosθSolve sin(θ)=1/2, θ in 0, 360), Find all the values of θ so that sin(θ)=1/2,how to solve trigonometric equations, blackpenredpen kash EduTech Pvt Ltd What are you looking for?




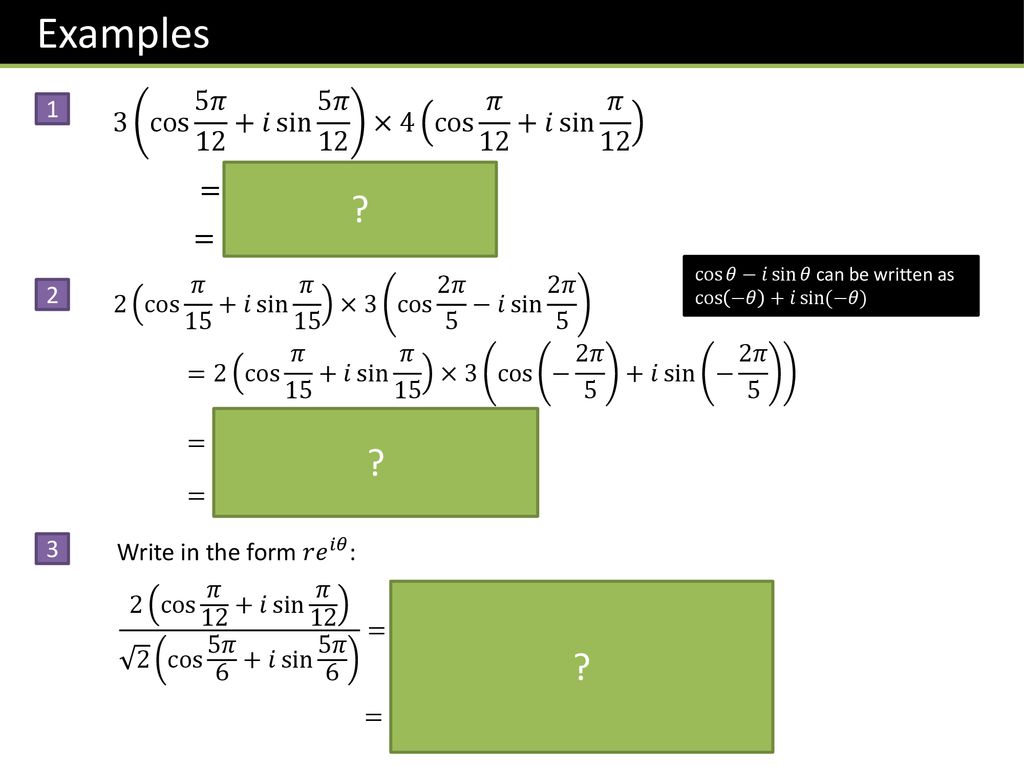
Example 16 Convert Z I 1 Cos Pi 3 I Sin Pi 3 Examples




If X A Cos 28 28 Sin 28 And Y A Sin 28 28 Cos 28 Find
The next value for which r = 0 r = 0 is θ = π / 2 θ = π / 2 This can be seen by solving the equation 3 sin (2 θ) = 0 3 sin (2 θ) = 0 for θ θ Therefore the values θ = 0 θ = 0 to θ = π / 2 θ = π / 2 trace out the first petal of the roseThe value of sin θcos θ will be greatest when θ=30∘ θ=45∘ θ=60∘ θ=90∘ Let fx=sin θcos θ=√2sinθπ4But−1≤sinθπ2≤1⇒−√2≤√2sinθπ4≤√2Hence the maximum value oFree trigonometric equation calculator solve trigonometric equations stepbystep




Engineering Mathematics I Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Find The Exact Value Of Tan 2 8 If Cos 8 3 Gauthmath
Sin theta=—323/325 and theta belongs to (π,3π/2) ie in 3rd quadrantHere sin theta is close to 1So,we can say theta is nearer to 90°Hence,(theta /2) belongs to 2nd quadrant where sine is positive and cosine is negative cos theta=√1sin^2 theta=—36/325=(0111) cos theta here is negative as theta is in 3rd quadrant0° θ 90° a)sin 2θ b)cos 2θ c)tan 2θ Please help! Then ∫ (sinn θ sinθ)^1/n cosθ/(sin^n1θ) dθ is equal to (where C is a constant of integration) asked in Mathematics by Niharika (756k points) jee mains 19;



Francisjosephcampena Weebly Com Uploads 1 7 8 6 Ched Precalculus Part5 Pdf
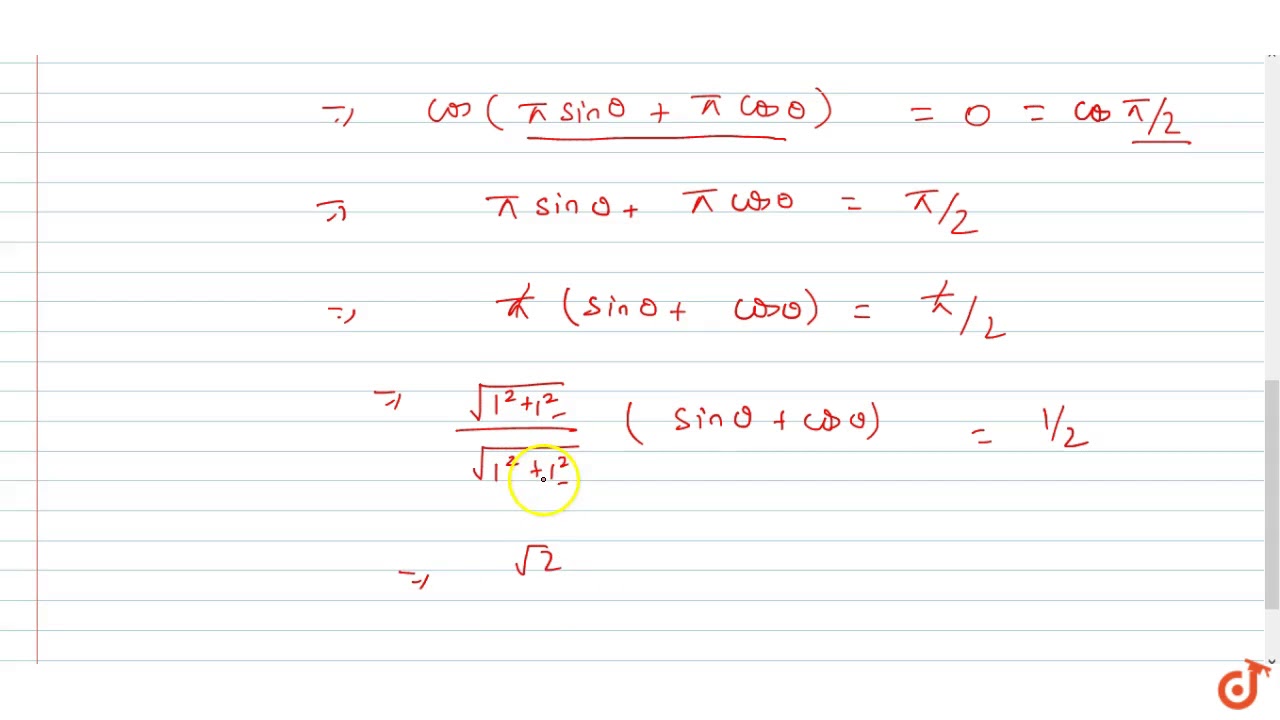



If Tan Pi Cos Theta Cot Pi Sin Theta Then Prove Cos Theta Pi 4 1 2 Sqrt2 Youtube
Start studying trig identities Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsExperts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high sin (θ) = 2/3 and π < θ < 3π/2 → cos (θ) < 0 ← (1) cos² (θ) sin² (θ) = 1Cos (θ1 θ2) = cosθ1 cosθ2 sinθ1 sinθ2 2) Obtain the values of sinθ and cos θ using Euler's formula , hence prove that, sin (θ 1 θ 2 ) = sinθ 1 cosθ 2 cosθ 1 sinθ 2




If Sin Pi Cos Theta Cos Pi Sin Theta Then Of The Value Cos Theta Pi 4 Is Youtube
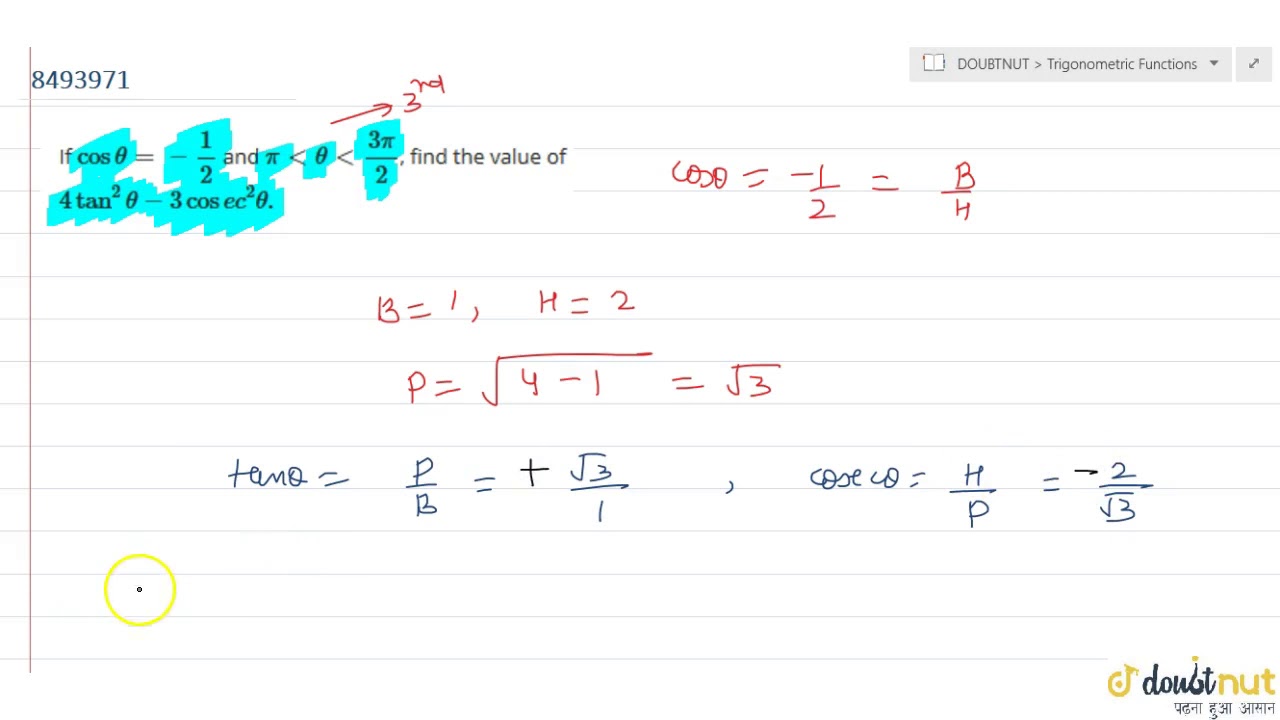



If Cos Theta 1 2 And Pi Lt Theta Lt 3pi 2 Find The Value Of 4 Tan 2 Theta 3 Cose Youtube
三角関数は周期関数なので、逆関数は多価関数である。 逆関数の性質から以下が成り立つ: =,() = / /ピタゴラスの定理 ピタゴラスの定理やオイラーの公式などから以下の基本的な関係が導ける 。 = ここで sin 2 θ は (sin(θ)) 2 を意味する。 この式を変形して、以下の式が導かれる: sin{π(π/2θ)} =sinπcos(π/2θ)cosπsin(π/2θ) =0×cos(π/2θ)(1)×sin(π/2θ) =sin(π/2θ) よって、最初の公式を用いて、 sin(π/2θ)=cosθ ナイス! yak********Give your answer as a fraction in simplified form Guest




Polar Curves Intersections Ppt Download




Use The Unit Circle To Evaluate The Six Trigonometric Functions Of 8 P Sin 8 Cos 8 Tan 8 Csc Brainly Com
Simplify\\tan^2(x)\cos^2(x)\cot^2(x)\sin^2(x) trigonometricsimplificationcalculator en Related Symbolab blog posts Spinning The Unit Circle (Evaluating Trig Functions ) If you've ever taken a ferris wheel ride then you know about periodic motion, you go up and down over and over I've tried to use the fact that $\tanθ = \frac{\sinθ}{\cosθ}$ and the property $\sin^2θ \cos^2θ = 1$ and trying to solve for sinθ but i'm running around in circles Also tried using the special triangles but the values i'm getting are way bigger than 1 trigonometry Share Cite 2 cosθ=−√2/3 , where π≤θ≤3π/2 tanβ=4/3 , where 0≤β≤π/2 What is the exact value of sin (θβ) ?




Verify The Following Identity 8 Cos 8 Frac Gauthmath




Fits To M Kp M Cos 8 K And Cos 8 Bℓ For The K ℓ ℓ Download Scientific Diagram



How To Find Theta For Cos Theta 1 2 Quora
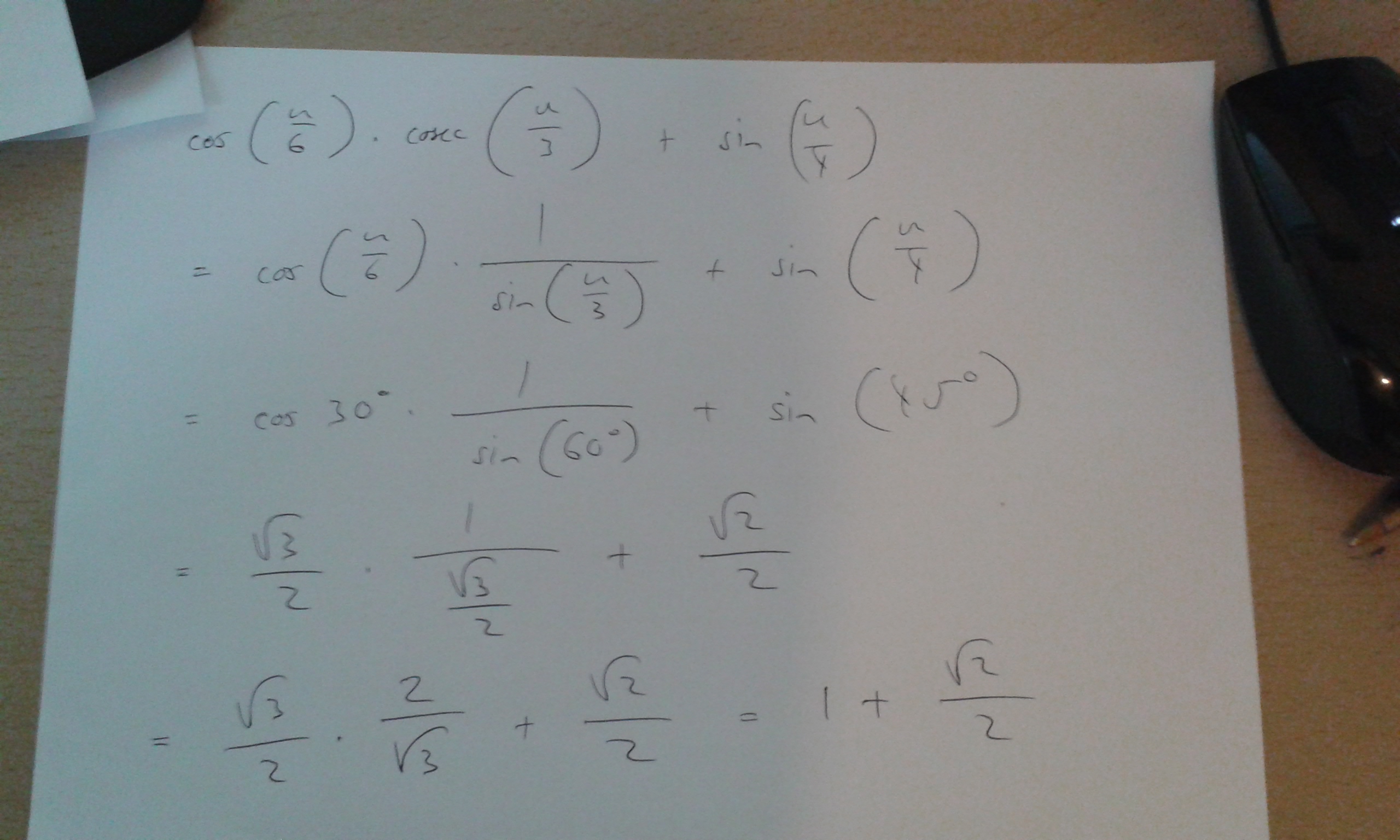



How Do You Determine The Exact Value For Cos Pi 6 Csc Pi 3 Sin Pi 4 Socratic



Q Tbn And9gcrhjnlyw8wv0cglkfihjo Yekht4szwsqxuapexkgb Lljycs L Usqp Cau



3



Mfg Inverse Trigonometric Functions




Unit Circle Sine And Cosine Functions Precalculus Ii
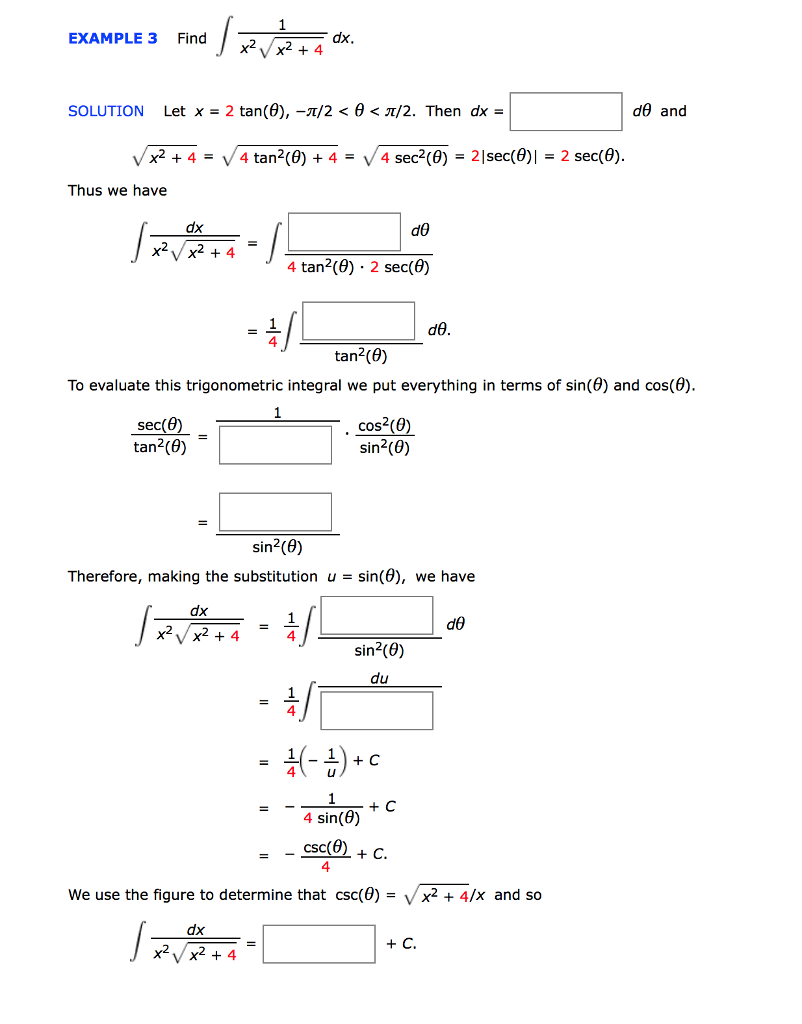



Example 3 Find Dx Solution Let X 2 Tan 8 Z 2 Chegg Com
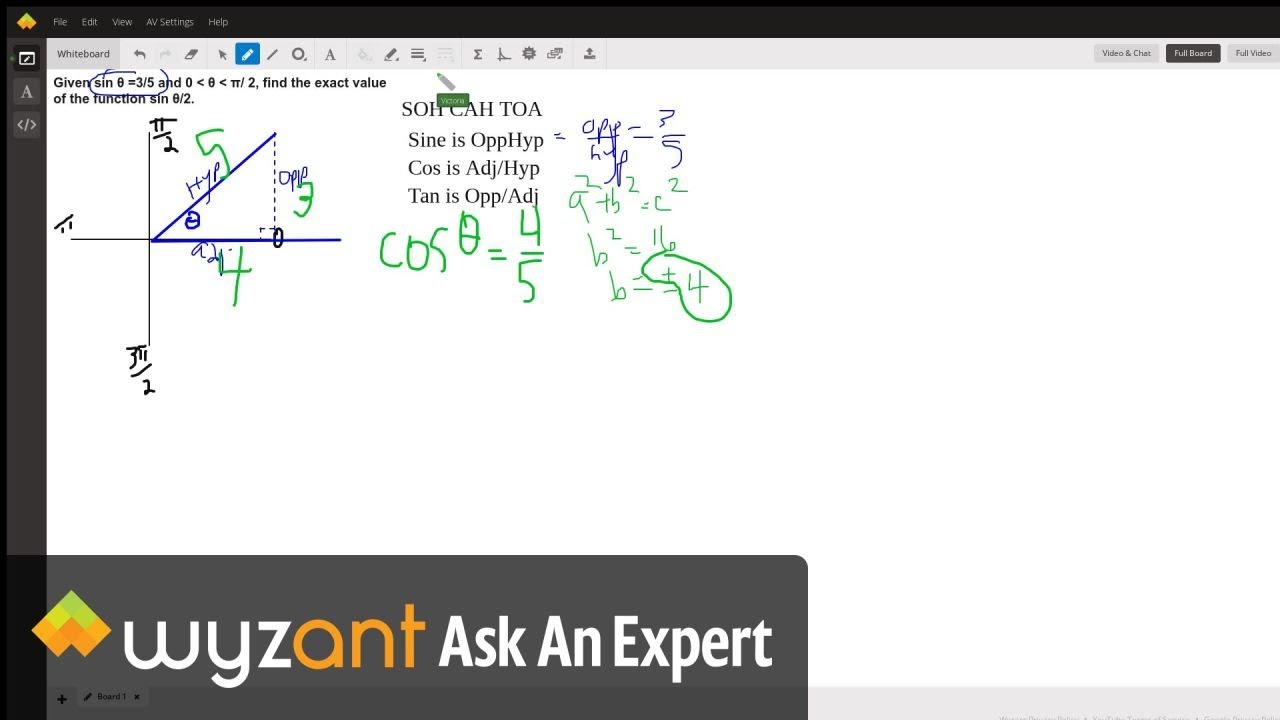



Given Sin 8 3 5 And 0 8 P 2 Find The Exact Value Of The Function Sin 8 2 Wyzant Ask An Expert



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions




Example 1 Evaluate X2 Solution Let X 9 Sin 8 Where Chegg Com




Limit Examples 1 Lim 8 Csc 8 Lim 8 Sin 8 1 Lim Sin 8 8 1 1 1




Trigonometric Functions Of Allied Angles Sin Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin 2 Pi Theta Sin Theta Cos 2 Pi Theta Cos Theta Tan 2 Pi Theta Tan Theta Sin Left Frac 3



Overview 1 2 This Chapter Is Divided Up Into Two Main Sections Ppt Download



What Is The Value Of Sin Pi 6 Socratic




Worksheet 1 Wsheet1 Sol Studocu




Sin Pi 2 X Sin Pi 2 Theta Youtube




Prove That Cos Pi Theta Cos Theta Cos Pi Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Cot Theta Youtube




Using The Identity Sin 2 8 Cos 2 8 1 Find Gauthmath




Int Pi 4 Pi 2 Costheta Cos Theta 2 Sin Theta 2 D Theta
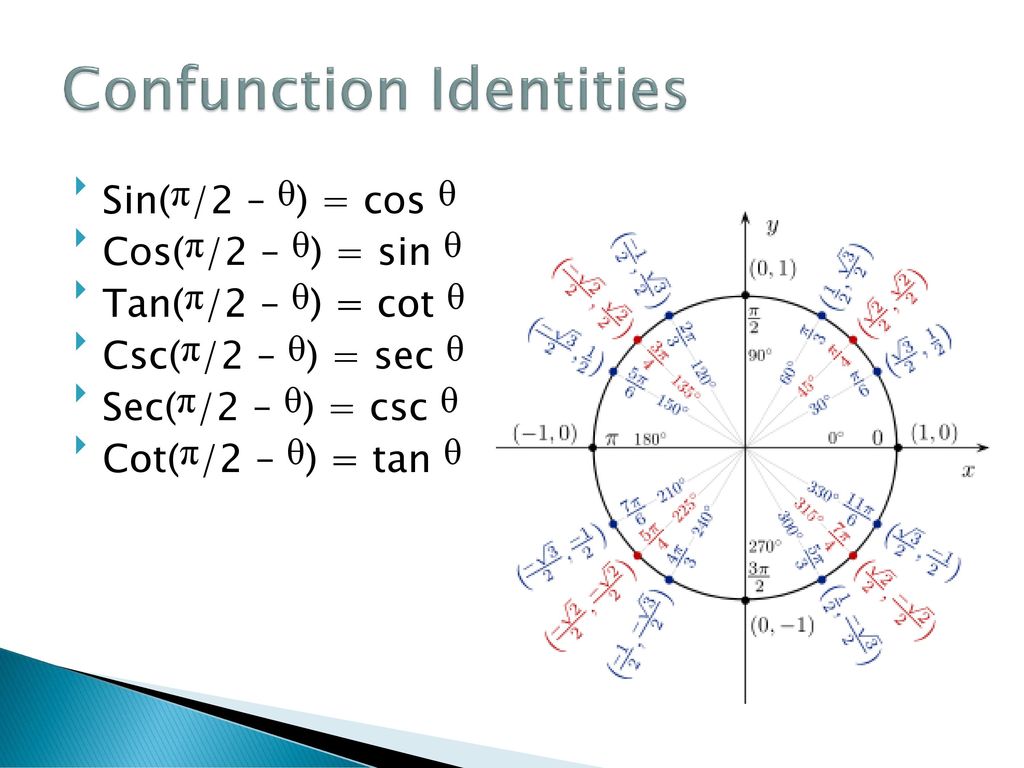



Chapter 5 Analytic Trigonometry 5 1 Fundamental Identities Ppt Download




Solving Sinusoidal Equations Of The Form Sin X D Video Khan Academy
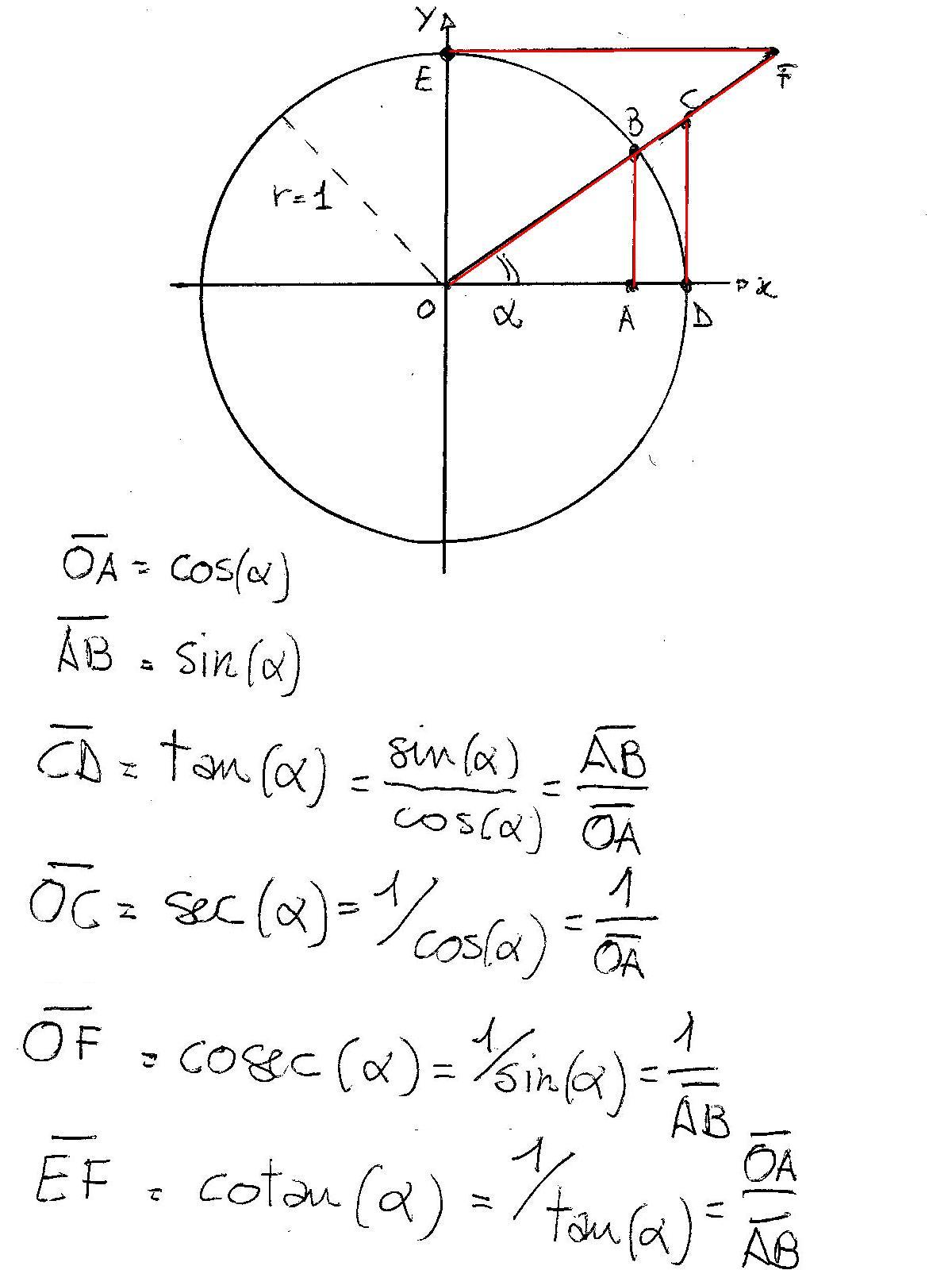



Basic Trigonometric Functions Trigonometry Socratic



1




Trigonometry Addition Formula For Rcos X A And R X A Ppt Download




Example 36 Find Dy Dx If X A Theta Sin Theta Y A
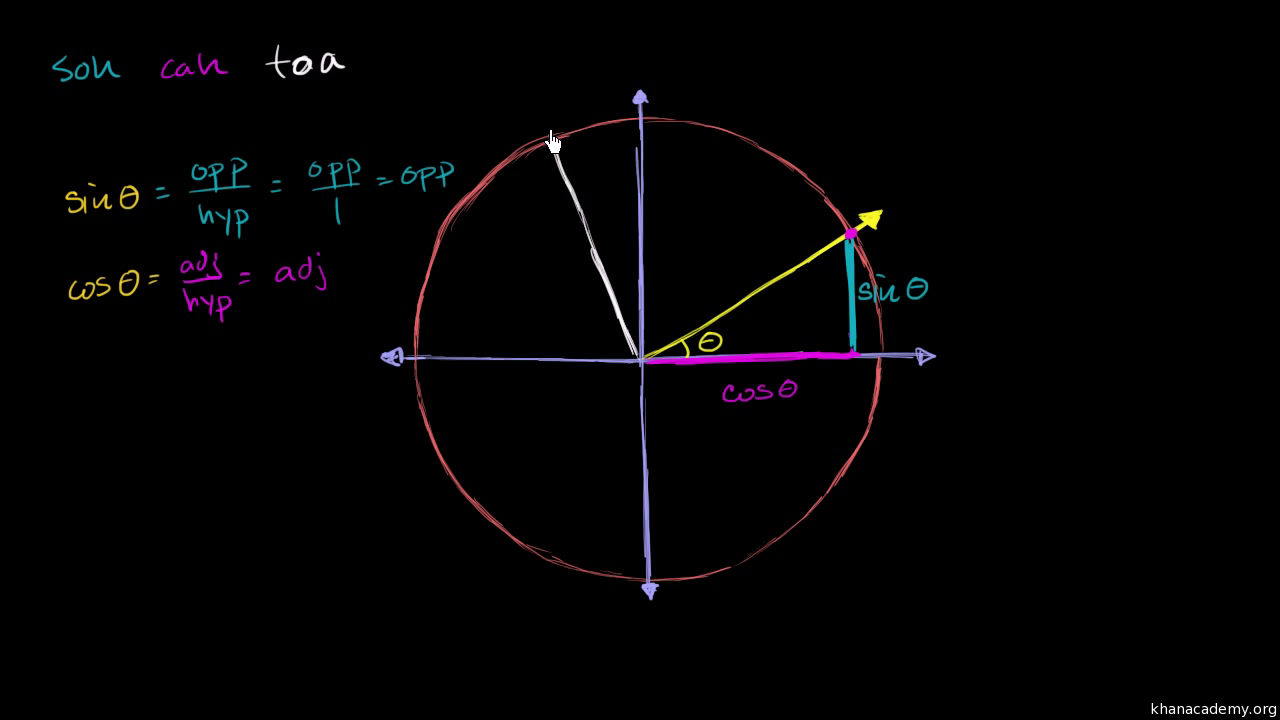



Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy



Trigonometry Without Pain



Solving Cos 8 1 And Cos 8 1 Video Khan Academy
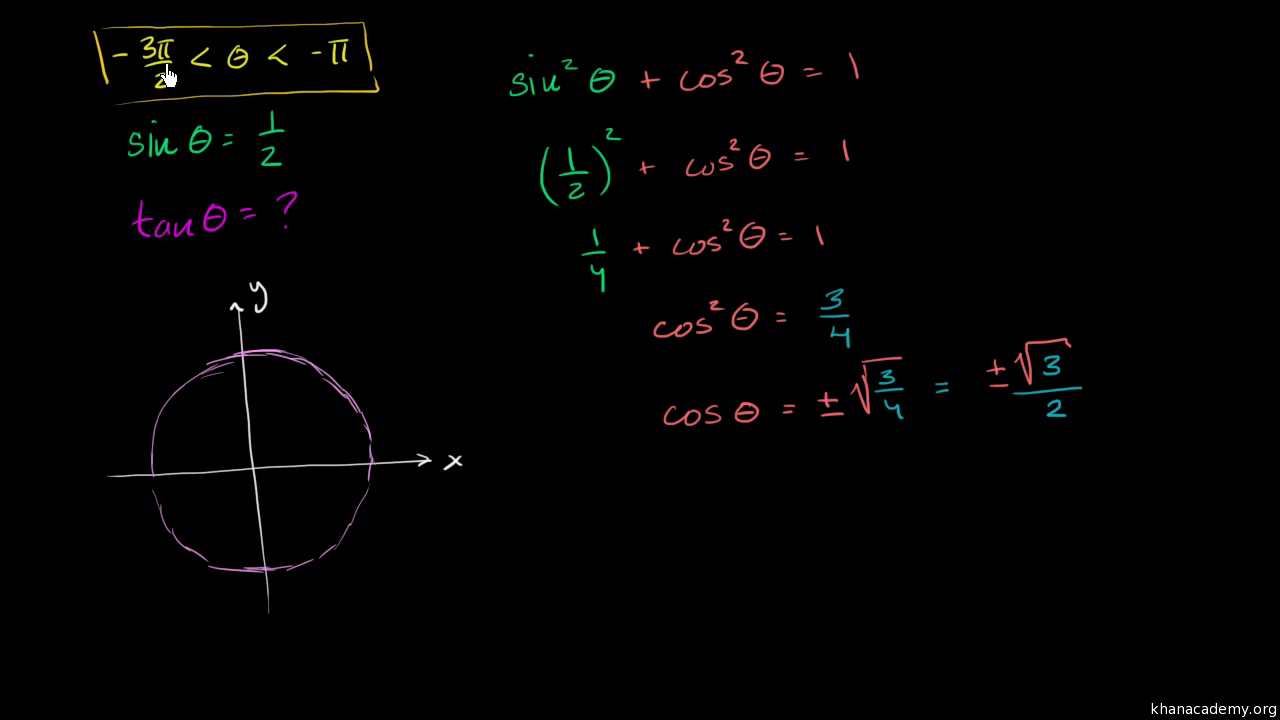



Using The Pythagorean Trig Identity Video Khan Academy



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions



Pplato Flap Math 3 3 Demoivre S Theorem And Complex Algebra




Math Polar Coordinates Ppt Download



Pmt Physicsandmathstutor Com Download Maths A Level C3 Topic Qs Edexcel Set 1 C3 trigonometry trigonometric identities Pdf




How To Find The General Solution Of Sin Left Theta Frac Pi 6 Right Cos 3 Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange



Pplato Flap Math 1 6 Trigonometric Functions




Given That Cos 8 24 25 And Frac 3 P 2 8 Gauthmath




For All Values Of Theta In 0 Pi 2 Show That Cos Sin Theta Gesin Costheta




If Sintheta Costheta Sqrt 2 Costheta Then The General Value Of Theta Is




Is The Function F X Cos X Even Odd Or Neither Socratic




If Cos Theta 1 2 And Pi Theta 3pi 2 Then Find The Value Of 4tan 2 Theta 3cosec 2 Theta




1 Trigonometry Further Mathematics Zimbabwe Zimsec Cambridge




Proved That 2 Sin P 4 Theta Costheta Sintheta Brainly In




If Alpha Is A Root Of 25cos 2theta 5costheta 12 0 Dfrac Pi 2 Alpha Pi Then Sin 28 Is Equal




If Tan Pcosx Cot Psinx Then Prove That Cos X P 4 1 2 2 Brainly In




The Value Of T A Nthetasin Pi 2 Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Is 1 B 1 C 1 2sin2theta D None Of These



7 4 Double Angle And Half Angle Identities Ppt Download



Http Www Southampton Ac Uk Cjg Eng1 Modules Old 07mod2 Pdf




Find The Area Enclosed By Circles R 3 Cos Theta And R 3 Sin Theta Mathematics Stack Exchange




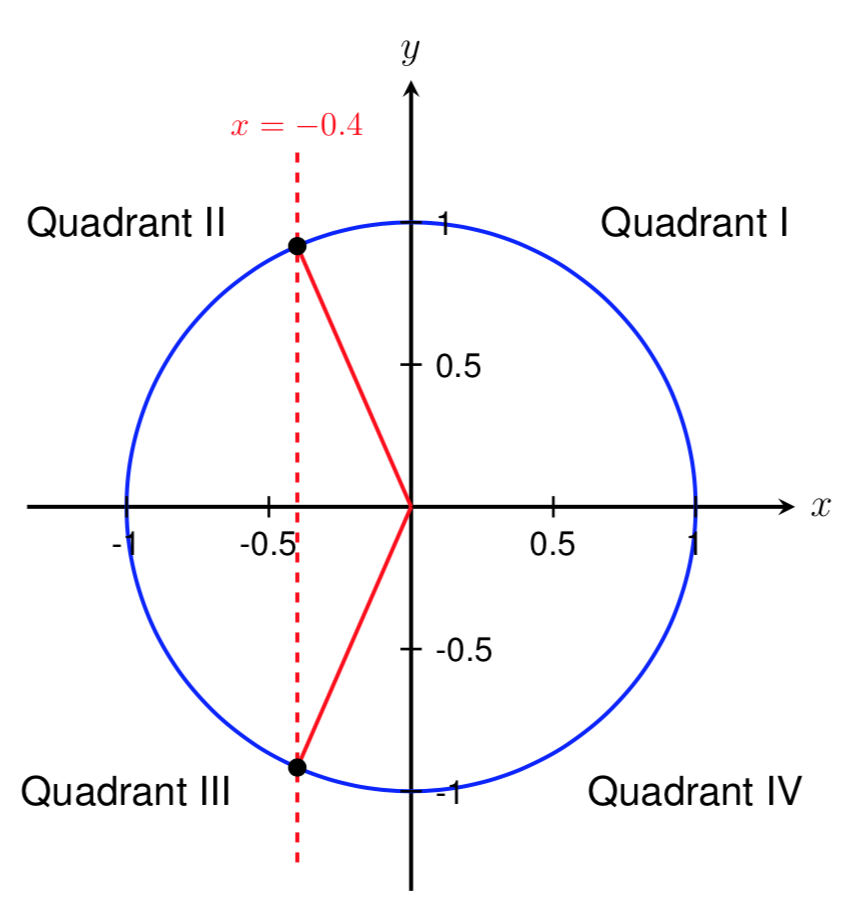
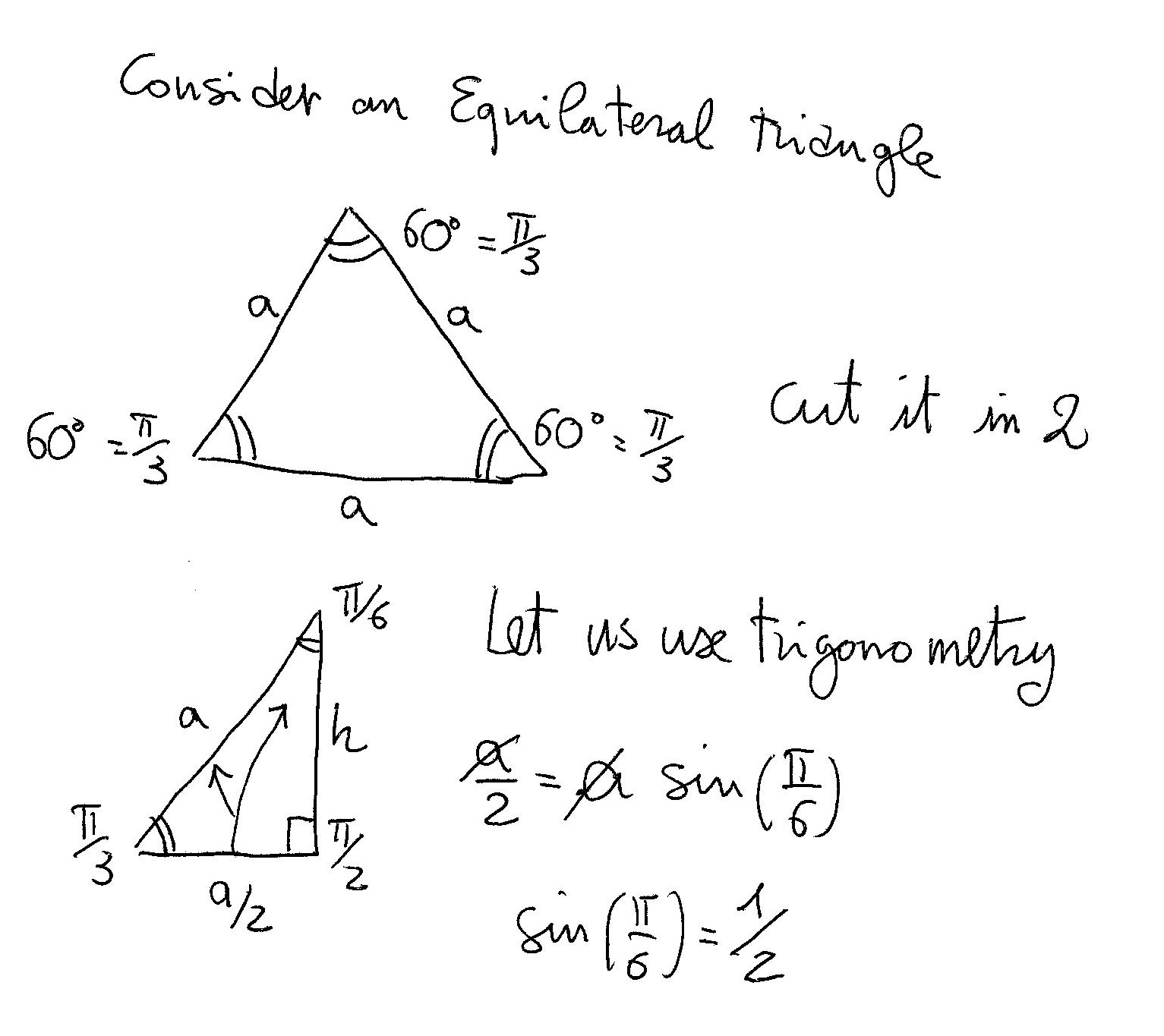
Geometric Proof Of Sin Frac Pi2 Theta Cos Theta For Theta Frac Pi2 Mathematics Stack Exchange




For All Theta In 0 Pi 2 Show That Cos Sintheta Sin Costheta



Sin 28 2sin 8 Cos 8 Proof Video Dailymotion



Corepure2 Chapter 1 Complex Numbers Ppt Download
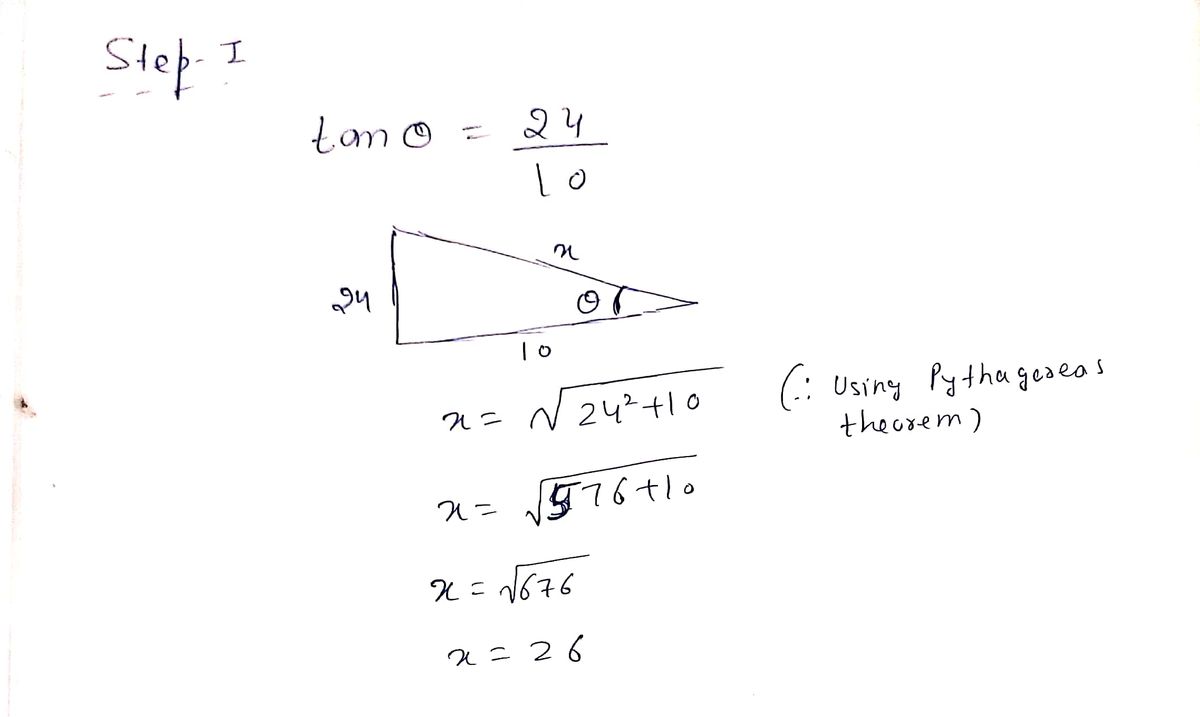



Answered If Tan 8 24 10 0 8 P 2 Bartleby




Ex 6 2 9 Prove That Y 4 Sin 2 Cos Theta Is Increasing




Hence Cos 8 Sin 8 0 5 Example 2 Pro Gauthmath



How To Verify Trig Identities Sin P 2 X Cos X Trigonometry Youtube




Using The Pythagorean Trig Identity Video Khan Academy



Reciprocal And Quotient Identities Reference Acute Angle The Cast Rule Negative Angle Identities Cofunction Identities Reduction Formulas Periodicity Identities 4 8 Sideway Output To




I Tan Picostheta Cot Pisintheta Then Cos Theta Pi 4 Is A 0 B 1 2sqrt 2 C 1 Sqrt 2 D None Of These



Mfg The Sine And Cosine Functions




Engineering Mathematics I Pages 51 100 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5



Www3 Nd Edu Nancy Math126 Info Trigformulas Pdf




Use Cos 5 Theta To Find The Roots Of X 16x 4 x 2 5 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange




81 X Dx Example 1 Evaluate X2 Solution Let X 9 Chegg Com




A Formula For Sin Pi 2 N Mathematics Stack Exchange



Trigonometry Reciprocal Identities Expii
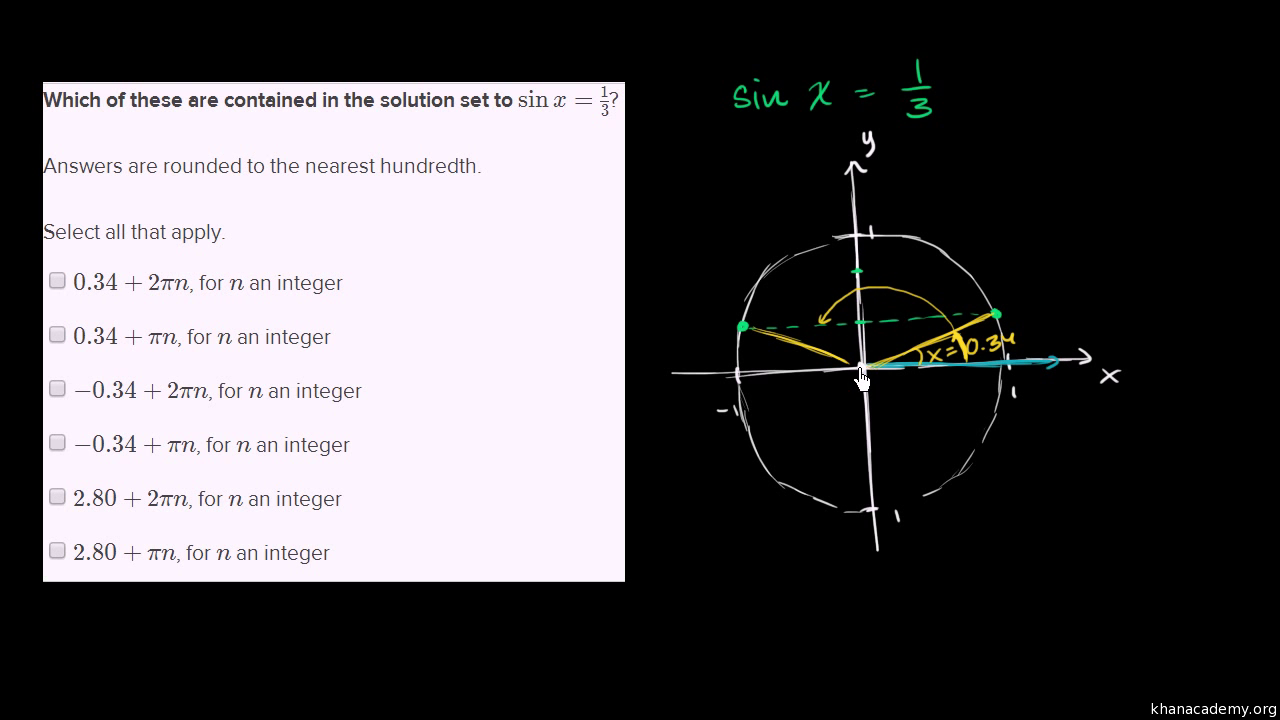



Solving Sinusoidal Equations Of The Form Sin X D Video Khan Academy




Find The Exact Values Of Sin 8 2 Cos 8 2 And Tan 8 2 For The Given Condition 3 Tan 8 3 180 8 90 Wyzant Ask An Expert




解説読んでも分かりません 教えてください Clear



Mckl2 Files Wordpress Com 15 11 Complex Number Fp1 Pdf




Find The Exact Values Of Sin 28 Cos 28 And Tan 28 Given The Following Sin 8 12 13 Where 8 Is In Quadrant Iv Wyzant Ask An Expert
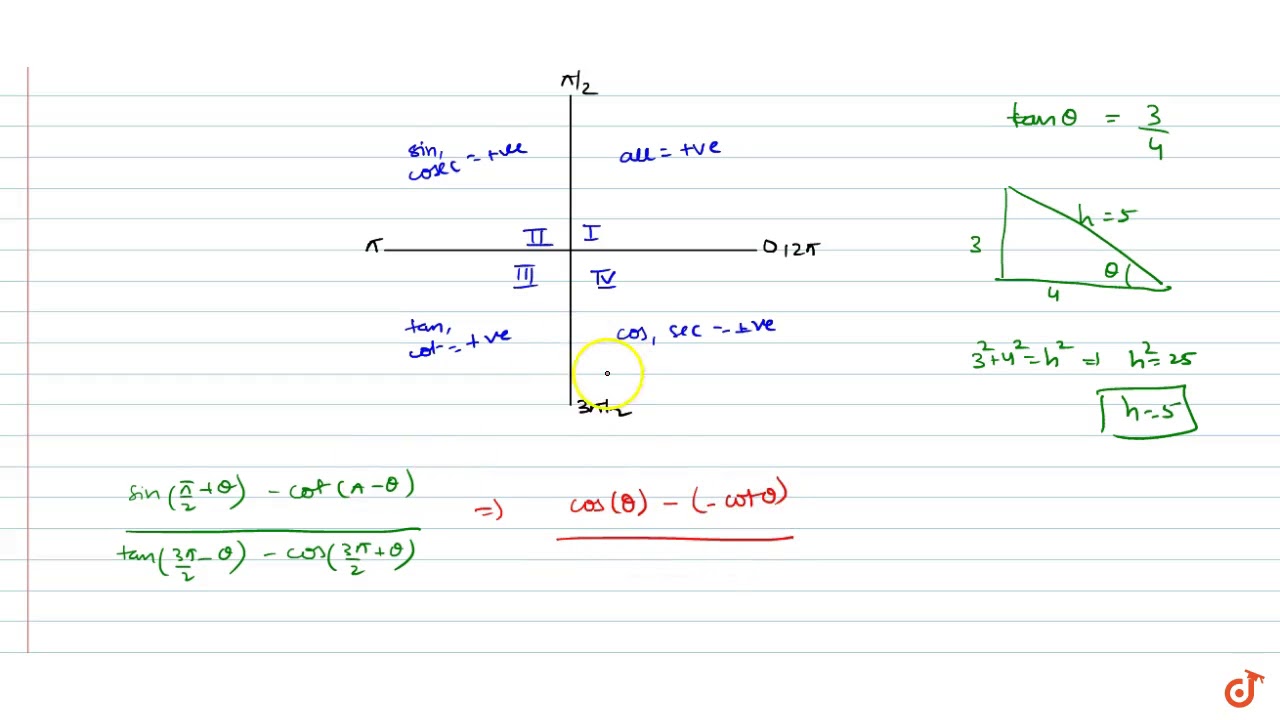



If Tan Theta 3 4 And Theta Is Not In First Quadrant Then Sin Pi 2 Theta Cot Pi Theta Youtube
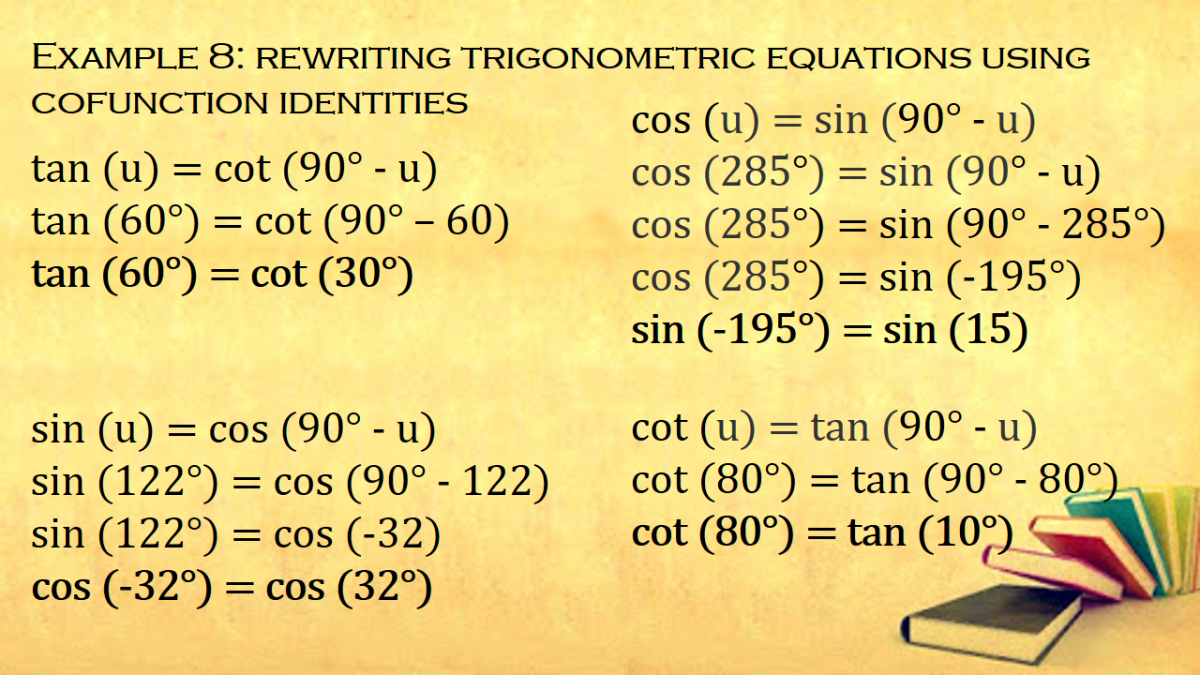



Cofunction Identities In Trigonometry With Proof And Examples Owlcation



3




Prove That Sin Theta Pi 6 Cos Theta Pi 3 Sqrt3 Sintheta Youtube
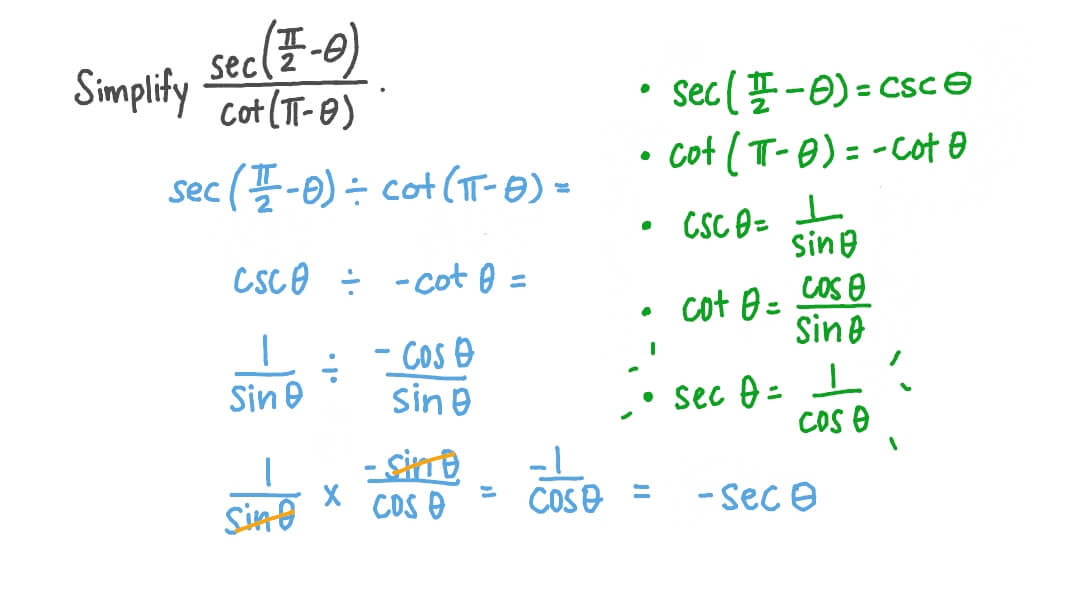



Question Video Using Periodic And Cofunction Identities To Simplify A Trigonometric Expression Nagwa




If Sin Theta 4 5 And Pi Lt Theta Lt 3pi 2 Find The Values Of All The Other Five Trigonometric Functions




4 Prove That 1 2 I Frac Sin 2 P Omega Gauthmath



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿